
财报术语Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities
流动负债
By Alicia Tuovila
Reviewed By Julius Mansa
Updated Jun 1, 2020
编写人:Alicia Tuovila
审核人:Julius Mansa
于2020年6月1日更新
What Are Current Liabilities?
什么是流动负债?
Current liabilities are a company's short-term financial obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle. An operating cycle, also referred to as the cash conversion cycle, is the time it takes a company to purchase inventory and convert it to cash from sales. An example of a current liability is money owed to suppliers in the form of accounts payable.
流动负债是指公司在一年之内或一个正常营业周期之内清偿的短期负债。营业周期,又称资金周转周期,指公司购入存货并通过销售将存货变现的周期。例如,公司应向供应商支付的款项(即应付账款),为流动负债。
Understanding Current Liabilities
了解流动负债
Current liabilities are typically settled using current assets, which are assets that are used up within one year. Current assets include cash or accounts receivables, which is money owed by customers for sales. The ratio of current assets to current liabilities is an important one in determining a company's ongoing ability to pay its debts as they are due.
流动负债通常通过流动资产予以清偿。流动资产指在一年内耗用的资产,包括现金或应收账款(即因销售商品等而应向客户收取的款项)。流动资产与流动负债的比率是衡量公司持续偿债能力的重要指标。
Accounts payable is typically one of the largest current liability accounts on a company's financial statements, and it represents unpaid supplier invoices. Companies try to match payment dates so that their accounts receivables are collected before the accounts payables are due to suppliers.
应付账款通常是公司财务报表中最大的流动负债科目之一,反映的是尚未付款的供应商发票。公司要尽力协调付款日期,以便在应付账款到期之前收回应收账款。
For example, a company might have 60-day terms for money owed to their supplier, which results in requiring their customers to pay within a 30-day term. Current liabilities can also be settled by creating a new current liability, such as a new short-term debt obligation.
例如,若公司需在60天内向供应商支付欠款,则该公司客户需在30天内向其支付欠款。流动负债也可以通过新的流动负债(如新的短期负债)予以清偿。
Key Takeaways
关键要点
· Current liabilities are a company's short-term financial obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle.
· 流动负债指公司在一年之内或一个正常营业周期之内清偿的短期负债。
· Current liabilities are typically settled using current assets, which are assets that are used up within one year.
· 流动负债通常通过流动资产(即一年内耗用的资产)予以清偿。
· Examples of current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term debt, dividends, and notes payable as well as income taxes owed.
· 流动负债包括应付账款、短期借款、应付股利、应付票据和应交税费。
Examples of Current Liabilities
流动负债示例
Below is a list of the most common current liabilities that are found on the balance sheet:
资产负债表中最常见的流动负债如下所示:
· Accounts payable
· 应付账款
· Short-term debt such as bank loans or commercial paper issued to fund operations
· 短期借款(如为资金运作而发放的银行贷款或出具的商业票据)
· Dividends payable
· 应付股利
· Notes payable—the principal portion of outstanding debt
· 应付票据——未偿债务本金
· Current portion of deferred revenue, such as prepayments by customers for work not completed or earned yet
· 递延收益中一年内到期的部分,如客户对尚未完成或盈利的工作支付的预付款
· Current maturities of long-term debt
· 长期负债中一年内到期的部分
· Interest payable on outstanding debts, including long-term obligations
· 未偿债务的应付利息,包括长期负债
· Income taxes owed within the next year
· 下一年内应交税费
Sometimes, companies use an account called "other current liabilities" as a catch-all line item on their balance sheets to include all other liabilities due within a year that are not classified elsewhere. Current liability accounts can vary by industry or according to various government regulations.
有时,公司会把未归类于其他项目的所有其他一年内到期的负债统归在资产负债表中的“其他流动负债”科目。各个行业或各种政府法规要求的流动负债科目各不相同。
How Current Liabilities are Used
流动负债的使用
Analysts and creditors often use the current ratio. The current ratio measures a company's ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations. The ratio, which is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities, shows how well a company manages its balance sheet to pay off its short-term debts and payables. It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables.
分析人员和债权人经常使用流动比率。流动比率用来衡量公司偿还其短期负债的能力。其计算方式是流动资产除以流动负债,目的是表明公司管理其资产负债表,清偿其短期负债和应付款项的能力。该比率向投资人和分析人员展示的是,公司资产负债表是否有足够的流动资产以清偿其短期负债和其他应付款项。
The quick ratio is the same formula as the current ratio, except it subtracts the value of total inventories beforehand. The quick ratio is a more conservative measure for liquidity since it only includes the current assets that can quickly be converted to cash to pay off current liabilities.
速动比率的公式与流动比率一样,即速动资产除以流动负债,其中速动资产等于流动资产减去总存货。由于速动资产只包含能够快速变现清偿流动负债的流动资产,用速动比率衡量偿债能力过于保守。
A number higher than one is ideal for both the current and quick ratios since it demonstrates there are more current assets to pay current short-term debts. However, if the number is too high, it could mean the company is not leveraging its assets as well as it otherwise could be.
理想情况下,流动比率和速动比率的数值均大于1,这说明公司有更多的流动资产偿还短期负债。但是,若数值过高,则可能说明公司资产运用不当。
Important: Although the current and quick ratios show how well a company converts its current assets to pay current liabilities, it's critical to compare the ratios to companies within the same industry.
重要提示:虽然流动比率和速动比率表明的是公司将其流动资产变现以偿还流动负债的能力,但关键是要将二者与同一行业内的其他公司进行比较。
The analysis of current liabilities is important to investors and creditors. Banks, for example, want to know before extending credit whether a company is collecting—or getting paid—for its accounts receivables in a timely manner. On the other hand, on-time payment of the company's payables is important as well. Both the current and quick ratios help with the analysis of a company's financial solvency and management of its current liabilities.
对于投资人和债权人而言,分析流动负债十分重要。例如,银行想知道在信贷展期之前公司是否及时收回其应收账款。另一方面,按时支付公司的应付款项也很重要。流动比率和速动比率有助于分析公司的财务清偿能力和对流动负债的管理能力。
Accounting for Current Liabilities
流动负债详解
When a company determines it received an economic benefit that must be paid within a year, it must immediately record a credit entry for a current liability. Depending on the nature of the received benefit, the company's accountants classify it as either an asset or expense, which will receive the debit entry.
若公司确定获得必须在一年之内支付的经济收益,必须立即贷记“流动负债”科目。根据所获收益的性质,公司的会计会将其分为资产或费用,计入借方。
For example, a large car manufacturer receives a shipment of exhaust systems from its vendors, with whom it must pay $10 million within the next 90 days. Because these materials are not immediately placed into production, the company's accountants record a credit entry to accounts payable and a debit entry to inventory, an asset account, for $10 million. When the company pays its balance due to suppliers, it debits accounts payable and credits cash for $10 million.
例如,一家大型汽车制造公司收到了供应商提供的排气系统,必须在接下来的90天内向其支付1000万美元。由于这些排气系统不会立即投入生产,该公司的会计会将该1000万美元贷记“应付账款”科目,借记“存货”科目(即资产类科目)。若该公司向供应商支付了结欠余额,会计会将该1000万美元借记“应付账款”科目,贷记“现金”科目。
Suppose a company receives tax preparation services from its external auditor, with whom it must pay $1 million within the next 60 days. The company's accountants record a $1 million debit entry to the audit expense account and a $1 million credit entry to the other current liabilities account. When a payment of $1 million is made, the company's accountant makes a $1 million debit entry to the other current liabilities account and a $1 million credit to the cash account.
假设公司外聘审计师负责其税务筹划事宜,必须在接下来的60天内向其支付100万美元。该公司的会计会将该100万美元借记“审计费用”科目,贷记“其他流动负债”科目。若该公司支付了该100万美元,会计会将该100万美元借记“其他流动负债”科目,贷记“现金”科目。
Real World Example of Current Liabilities
有关流动负债的真实示例
Below is a current liabilities example using the consolidated balance sheet of Macy's Inc. (M) from the company's 10Q report reported on August 03, 2019.
以美国梅西百货公司(Macy's Inc. (M))的10Q季度报表(时间:2019年8月3日)中的合并资产负债表为例,如下所示:
· We can see the company had $6 million in short-term debt for the period.
· 我们可以看出该公司的本期短期负债为600万美元。
· Accounts payable was broken up into two parts, including merchandise payables totaling $1.674 billion and other accounts payable and accrued liabilities totaling $2.739 billion.
· 应付账款分为两部分,即商品应付账款(合计16.74亿美元),以及其他应付账款和应计负债(合计27.39亿美元)。
· Macy's had $20 million in taxes payable.
· 该公司的应交税费为2000万美元。
· Total liabilities for August 2019 was $4.439 billion, which was nearly unchanged when compared to the $4.481 billion for the same accounting period from one year earlier.
· 2019年8月的流动负债合计44.39亿美元,相较于2018年的同一会计期间,即44.81亿美元,基本维持不变。
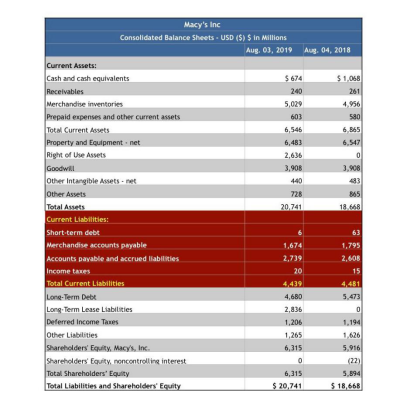
Macy's Current Liabilities Example. Investopedia
美国梅西百货公司的流动负债示例(来源:Investopedia)
|
美国梅西百货公司合并资产负债表项目英中对照 |
|
|
Macy's Inc |
美国梅西百货公司 |
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets - USD ($) $ in Millions |
合并资产负债表(单位:百万美元) |
|
Aug. 03, 2019 |
2019年8月3日 |
|
Aug. 04, 2018 |
2018年8月4日 |
|
Current Assets |
流动资本 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
现金及现金等价物 |
|
Receivables |
应收账款 |
|
Merchandise inventories |
库存商品 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
预付款项 |
|
Total Current Assets |
流动资产合计 |
|
Property and Equipment - net |
固定资产净额 |
|
Right of Use Assets |
使用权资产 |
|
Goodwill |
商誉 |
|
Other Intangible Assets - net |
其他无形资产净额 |
|
Other Assets |
其他资产 |
|
Total Assets |
资产总计 |
|
Current Liabilities |
流动负债 |
|
Short-term debt |
短期负债 |
|
Merchandise accounts payable |
商品应付账款 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
应付账款和应计负债 |
|
Income taxes |
所得税 |
|
Total Current Liabilities |
流动负债合计 |
|
Long-Term debt |
长期负债 |
|
Long-Term Lease Liabilities |
长期租赁负债 |
|
Deferred Income Taxes |
递延所得税负债 |
|
Other Liabilities |
其他负债 |
|
Shareholders’ Equity, Macy's Inc. |
股东权益(美国梅西百货公司) |
|
Shareholders’ Equity, noncontrolling interest |
股东权益(少数股东) |
|
Total Shareholders’ Equity |
股东权益合计 |
|
Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity |
负债和股东权益合计 |




